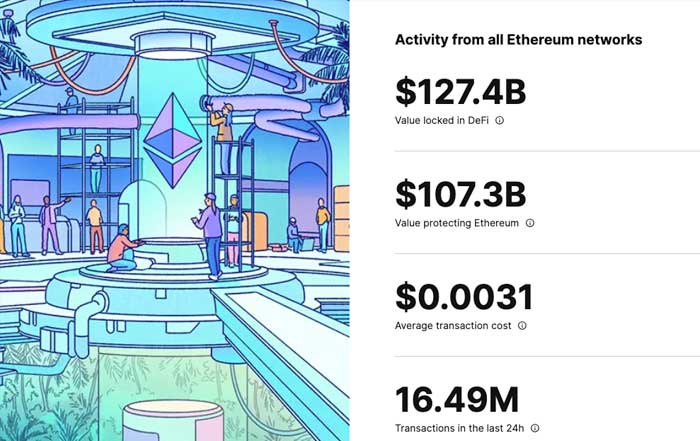
Decentralized Finance in 2026: Strategic Opportunities and Risks for Global Business
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has moved from experimental frontier to strategic consideration for executives and founders across the world by 2026. What began as a niche segment within the cryptocurrency ecosystem has matured into a complex, interoperable financial infrastructure that increasingly interacts with traditional markets and regulatory systems. For the readership of dailybusinesss.com, which spans leaders focused on AI, finance, business strategy, crypto, economics, employment, founders, investment, markets, and the future of trade, DeFi now represents less a speculative trend and more a set of tools and paradigms that can reshape how capital is raised, managed, and deployed across global value chains.
As the post-2020 cycles of exuberance, correction, and consolidation have played out, DeFi has demonstrated resilience and adaptability. Institutional participation from firms such as BlackRock, Fidelity, and Goldman Sachs, alongside the persistent innovation of crypto-native teams, has pushed decentralized protocols toward higher standards of security, governance, and compliance. At the same time, regulators in the United States, Europe, Asia, and other regions have refined their positions, providing a clearer-if still evolving-framework within which businesses can operate. For decision-makers reading dailybusinesss.com, the central question in 2026 is no longer whether DeFi matters, but how to harness its strengths without compromising on risk management, regulatory alignment, or corporate reputation.
From Experiment to Infrastructure: The Maturation of DeFi
The early DeFi wave between 2019 and 2022 was characterized by rapid experimentation, outsized yields, and frequent technical and economic failures. By 2024 and 2025, however, the sector had entered a more disciplined phase. Core infrastructure such as Ethereum's proof-of-stake network, accessible via ethereum.org, and high-throughput Layer 2 solutions laid the groundwork for scalable, low-cost financial transactions that now underpin both retail and institutional use cases. Competing smart contract platforms like Solana, Avalanche, and Polygon diversified the landscape, each optimizing for different trade-offs between speed, decentralization, and security.
This foundation enabled DeFi protocols to evolve from simple lending pools and automated market makers into sophisticated platforms offering collateralized lending, options and futures, on-chain asset management, and tokenized representations of real-world assets. The concept of composability-where protocols interlock like "money legos"-has become a defining feature, allowing businesses and developers to build complex financial workflows from standardized primitives. A company can, for instance, tokenize receivables, use those tokens as collateral on a lending platform, hedge currency exposure via a decentralized derivatives protocol, and settle cross-border invoices in stablecoins, all through interoperable smart contracts.
For readers of dailybusinesss.com, this composability is particularly relevant because it mirrors the modularization seen in modern software and cloud architectures. Just as enterprises moved from monolithic systems to microservices, financial operations are gradually shifting from vertically integrated banking stacks to horizontally integrated protocol layers. The result is a more flexible environment where businesses can select best-in-class components for payments, liquidity, risk management, and investment, rather than relying solely on a single financial institution.
Core Building Blocks: Stablecoins, Lending, DEXs, and Oracles
At the heart of the DeFi ecosystem in 2026 are several core components that now function with increasing reliability and scale. Stablecoins have become the primary transactional medium on public blockchains, with regulated offerings such as USDC and EURC issued by Circle and others emerging as preferred instruments for corporates and fintechs. Central bank digital currency pilots and limited rollouts in regions such as Europe and Asia coexist with private stablecoins, while organizations monitor developments through resources like the Bank for International Settlements and the International Monetary Fund.
Lending protocols, originally exemplified by platforms such as Aave and Compound, have evolved into multi-asset, risk-tiered markets where institutions can participate via permissioned pools that meet Know-Your-Customer and Anti-Money Laundering standards. Credit risk models have become more sophisticated, blending on-chain collateralization data with off-chain credit scoring, sometimes informed by AI-driven analytics. Businesses can now access liquidity without traditional banking intermediaries, posting tokenized treasuries or receivables as collateral. For executives exploring new treasury strategies, introductory overviews on DeFi and digital assets at dailybusinesss.com provide helpful context.
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) have likewise matured. Automated Market Maker models pioneered by Uniswap, accessible at uniswap.org, and later refined by platforms such as Curve and Balancer, have been complemented by on-chain order book systems that support institutional-grade trading. Liquidity incentives have shifted from unsustainably high "yield farming" rewards toward fee-driven, volume-based economics. For many businesses, DEXs now serve as key venues for price discovery and hedging of tokenized assets, including tokenized treasury bills, commodities, and carbon credits.
None of this would function reliably without robust oracle infrastructure. Decentralized oracle networks such as Chainlink, detailed at chain.link, supply real-time price feeds, rate benchmarks, weather data, and other off-chain information to smart contracts. For tokenized real estate, trade finance instruments, or insurance products, oracles enable automated payouts and re-pricing based on verifiable external events. Their importance to systemic stability is increasingly recognized by regulators and risk managers, who view oracle quality as a critical factor in assessing protocol resilience.
Real-World Asset Tokenization and Institutional On-Ramp
One of the most significant developments between 2023 and 2026 has been the acceleration of real-world asset (RWA) tokenization. Governments, banks, asset managers, and corporates have begun to issue tokenized versions of government bonds, corporate debt, money market funds, and real estate, often under regulated frameworks. Platforms backed by institutions such as JPMorgan, HSBC, and Societe Generale have demonstrated that tokenized assets can settle faster, trade more flexibly, and be integrated into DeFi liquidity pools while still complying with existing securities laws.
This convergence is reshaping capital markets. Businesses can now raise funds by issuing tokenized debt instruments that are instantly tradable on regulated secondary markets, reducing friction and broadening the investor base. Fractionalization enables smaller investors to participate in asset classes previously accessible only to large institutions, aligning with broader goals of financial inclusion promoted by organizations like the World Bank and OECD. For founders and growth-stage companies, tokenization offers an alternative to conventional venture and private equity routes, complementing the perspectives shared in the founders and investment coverage on dailybusinesss.com.
In parallel, tokenization has begun to intersect with sustainability and ESG agendas. Voluntary carbon markets and renewable energy certificates are increasingly represented as on-chain tokens, enabling transparent tracking, retirement, and secondary trading. DeFi infrastructure allows these tokens to be used as collateral or embedded into structured products that support climate-aligned investment strategies. Executives can explore broader sustainability implications through resources such as the United Nations Environment Programme and complement that with targeted analysis on sustainable business models at dailybusinesss.com.
DeFi, AI, and Data-Driven Finance
For an audience that closely follows developments in AI and advanced analytics, the intersection of DeFi and AI is particularly relevant in 2026. The transparent, machine-readable nature of on-chain data has created fertile ground for AI-driven risk models, liquidity optimization, and algorithmic trading strategies. Hedge funds, asset managers, and corporate treasuries now deploy AI agents that continuously monitor DeFi markets, assess counterparty risk, and rebalance positions across lending pools and DEXs.
AI also plays a growing role in compliance and fraud detection. Machine learning models trained on blockchain transaction histories can flag anomalous patterns, support transaction monitoring obligations, and help organizations meet evolving regulatory expectations in the United States, Europe, and Asia. Guidance from institutions such as the Financial Action Task Force informs how DeFi platforms and their enterprise users implement risk-based controls while preserving the openness that defines public blockchains.
For businesses integrating DeFi into operational finance, AI can automate treasury allocations based on real-time cash flow forecasts, FX exposure, and risk appetite. An enterprise might, for example, maintain a rules-based treasury policy that allocates a portion of idle cash into tokenized T-bill pools, stablecoin lending markets, or on-chain money market funds, with AI systems continuously adjusting allocations in response to market conditions. Readers seeking to understand how AI is re-shaping corporate decision-making can consult the AI-focused insights on dailybusinesss.com, where DeFi is increasingly treated as a natural extension of digital transformation.
Cross-Border Payments, Trade, and Supply Chain Finance
In 2026, cross-border payments and trade finance remain among the most compelling enterprise use cases for DeFi. Traditional correspondent banking networks often impose high fees, long settlement times, and limited transparency, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises operating across Africa, Asia, and South America. Stablecoin-based payment rails and on-chain settlement networks now offer near-real-time transfers at materially lower cost, with clear visibility into transaction status.
Trade finance is undergoing similar change. Tokenized invoices, bills of lading, and warehouse receipts can be financed via DeFi lending pools, with repayment flows automated through smart contracts once goods are delivered and verified. IoT devices and digital identity frameworks, often aligned with standards promoted by bodies like the World Trade Organization, feed data into these contracts, reducing fraud and accelerating working capital cycles. For export-oriented businesses in regions such as Southeast Asia, Europe, and Latin America, DeFi-enabled trade finance can be a strategic differentiator, shortening cash conversion cycles and expanding access to global liquidity.
These developments align with the broader coverage of global trade and markets on dailybusinesss.com, where readers can explore complementary analysis in the trade and markets sections. As more banks and logistics providers integrate blockchain-based documentation and settlement systems, the line between "DeFi" and "digital trade infrastructure" continues to blur.
Regulatory Normalization and Compliance by 2026
By 2026, regulators in major jurisdictions have moved beyond the early, often reactive stance toward DeFi and digital assets. While approaches still vary across the United States, European Union, United Kingdom, Singapore, and other leading financial centers, several trends are clear. First, there is a growing distinction between permissionless, retail-oriented protocols and permissioned or "whitelisted" environments designed for institutional users. Second, stablecoins and tokenized securities are increasingly governed under updated versions of existing payment and securities regulations rather than entirely new regimes.
The European Union's Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) framework and subsequent guidance on tokenized financial instruments have provided a template for other regions. In the United States, a combination of Securities and Exchange Commission interpretations, Commodity Futures Trading Commission oversight, and state-level licensing has produced a patchwork that large enterprises navigate with specialized legal counsel. Organizations monitor developments through trusted sources such as ESMA and the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, recognizing that regulatory clarity is both a constraint and an enabler.
For businesses, the practical implication is that DeFi adoption now requires structured governance. Internal policies must address protocol selection, counterparty risk, custody arrangements, accounting treatment, tax reporting, and sanctions compliance. Many corporates have established dedicated digital asset committees, combining expertise from treasury, legal, risk, IT, and sustainability teams. As the regulatory environment stabilizes, insurers and auditors have become more comfortable supporting DeFi-related activities, provided that clients adhere to well-documented controls and use vetted platforms.
The readership of dailybusinesss.com, particularly those following finance and economics, will recognize that this regulatory normalization is a prerequisite for large-scale institutional adoption. It reduces the legal uncertainty premium that previously deterred conservative capital allocators such as pension funds, sovereign wealth funds, and insurance companies from meaningful engagement with DeFi.
Risk, Security, and Trust: The Evolving Governance of DeFi
Despite the progress, DeFi remains a high-velocity environment where technical, economic, and governance risks must be actively managed. Smart contract exploits, oracle manipulation, governance attacks, and liquidity crises have not disappeared; instead, they have become better understood and, in many cases, more sophisticated. Security best practices now include multi-layered audits, formal verification, bug bounty programs, and real-time monitoring. Specialized security firms and threat intelligence providers have become critical partners for both protocols and institutional users.
Governance presents another dimension of risk and opportunity. Many leading DeFi platforms operate as decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), where governance tokens confer voting rights over protocol parameters, fee structures, and strategic initiatives. While this community-driven model supports adaptability and user alignment, it can also concentrate power among large token holders and create uncertainty for enterprise users who depend on predictable policies. Some jurisdictions, including segments of the United States and Europe, have begun to recognize DAOs as legal entities, offering clearer liability frameworks but also attaching regulatory obligations.
To build trust, a growing number of protocols now adopt hybrid governance models that combine token-based voting with expert councils, risk committees, and formal disclosure requirements. This evolution resembles the progression of early stock exchanges and mutual funds toward more robust corporate governance. For executives evaluating DeFi partnerships, the quality of governance-transparency, accountability, and responsiveness-has become as important as technical performance or yield metrics. Independent research from organizations like the Blockchain Association and analytical platforms such as Messari or Token Terminal helps businesses evaluate governance quality alongside financial and technical indicators.
Strategic Adoption: How Businesses Are Using DeFi in Practice
By 2026, leading organizations across the United States, Europe, Asia, and other regions have moved beyond pilots to targeted, production-grade DeFi integrations. Multinational corporations use tokenized cash and short-duration government securities as part of their liquidity management strategies, often via permissioned pools that comply with institutional onboarding standards. Fintechs and neobanks embed DeFi yield products behind familiar interfaces, offering customers access to regulated, on-chain money market funds or tokenized savings products without exposing them directly to protocol complexity.
Exporters and importers integrate stablecoin-based settlement into their trade flows, particularly in corridors where local banking infrastructure is costly or unreliable. Real estate investment firms tokenize fund units or property portfolios, enabling fractional ownership and providing secondary market liquidity that traditional structures struggle to match. In emerging markets, microfinance institutions and alternative lenders experiment with on-chain credit scoring and collateralization, connecting local borrowers to global pools of capital.
For the dailybusinesss.com audience, these use cases translate into concrete strategic levers. CFOs consider DeFi as an extension of corporate treasury; COOs view it as a tool for supply chain optimization; CTOs integrate blockchain rails into enterprise architectures; founders leverage tokenization to access global investors; and sustainability officers explore on-chain carbon and ESG instruments. Insights across business strategy, investment, and world economic trends on dailybusinesss.com increasingly intersect with DeFi themes, reflecting this multi-functional relevance.
Regional Dynamics and Global Competition
The geography of DeFi in 2026 is shaped by regulatory posture, technological capacity, and capital markets depth. The United States remains a center for protocol development, venture capital, and institutional experimentation, even as regulatory debates continue. The United Kingdom, Switzerland, and the European Union have positioned themselves as hubs for regulated tokenization and institutional digital asset markets, with jurisdictions like Switzerland and Luxembourg hosting a growing number of tokenized funds and structured products.
In Asia, Singapore, Hong Kong, and South Korea have emerged as leading centers for institutional DeFi and Web3 innovation, leveraging supportive regulatory frameworks and strong banking sectors. Japan continues to refine its digital asset regulations, while China focuses more on permissioned blockchain and central bank digital currency infrastructure. In the Middle East, financial centers such as Dubai and Abu Dhabi are attracting crypto and DeFi firms with bespoke regulatory regimes. Across Africa and Latin America, stablecoin adoption and DeFi-enabled remittances are increasingly important in countries facing currency volatility or limited banking penetration.
This regional competition is influencing where protocols incorporate, where talent migrates, and where capital flows. Businesses evaluating DeFi strategies must therefore consider jurisdictional risk alongside protocol-level considerations. Cross-border operations may require a multi-hub approach, using different platforms and structures in the United States, Europe, and Asia to remain compliant while maximizing access to innovation.
The Road Ahead: DeFi as a Layer of Global Finance
Looking toward the late 2020s, DeFi appears set to become a durable layer of global finance rather than a transient phenomenon. Its role will likely be most pronounced in areas where transparency, programmability, and global accessibility deliver clear advantages: cross-border payments, asset tokenization, programmable trade finance, composable capital markets, and machine-to-machine transactions in IoT-driven industries. At the same time, traditional financial institutions will continue to play central roles in credit intermediation, complex risk transformation, and regulatory engagement.
For the global business community that turns to dailybusinesss.com for strategic insight, the imperative is to treat DeFi neither as a panacea nor as a peripheral curiosity, but as a toolkit that can be selectively integrated into broader digital, financial, and sustainability strategies. Executives and founders who invest in understanding the underlying mechanisms, regulatory context, and risk dynamics will be better positioned to capture upside while avoiding avoidable pitfalls.
As resources from organizations such as the World Economic Forum, the Bank for International Settlements, and leading academic centers continue to refine best practices, and as dailybusinesss.com expands its coverage of AI, crypto, markets, and sustainable finance, the knowledge base around DeFi will become more accessible to non-specialists. In this environment, the competitive advantage will accrue not simply to those who adopt DeFi first, but to those who adopt it most intelligently-aligning decentralized finance with corporate purpose, stakeholder trust, and long-term value creation in an increasingly interconnected global economy.